This article is the second of a series on the public campaigning strategies that contributed to achieving a major legal victory for Trans people in Spain. It is still based on the report by La Interseccion.
Analysing the conversations on social media
As part of the initial investigation to prepare for the collective campaign supporting trans people, the campaign team analysed the conversation on Twitter.
Between August 1, 2021, and June 1, 2022, 231K tweets were captured mentioning trans and non-binary people, gender diversity laws, inclusive sexual education, and inclusive language. Twitter users were grouped according to their relationships (that is, who retweets whom), and the pattern that emerged helped identify seven major communities. Five of these, about 41% of users analysed, appeared to favour LGTBI rights and generated 49% of all tweets analysed. Furthermore, two communities seemed to be against LGBTI rights. They accounted for 33% of the tweets and 24% of the users.

Identifying main communities along their narratives
After analysing the contents of the tweets, focusing on those with the greatest reach (most retweets), the team was able to summarise and draw some conclusions about the main narratives circulating within each community.
Communities opposing LGBTI rights
Two main opposition communities were identified, making up 24% of the users and 33% of the tweets analysed.
The first is a group of far-right users, about 15% of the accounts analysed, who generated 12% of all opposition tweets. They chose to focus their narrative on society’s perceived cultural decline because it is “distracted by absurd considerations on gender.” The accounts of the leading representatives of the Spanish Far-right party, Vox, seemed to have taken a strategic stance of silence; however, opposition tweets came from prominent accounts, for example, journalists and other informal accounts related to far-right ecosystems.
The second opposition community was noted to be specifically trans-exclusionary. These users were about 9% of all accounts analysed and generated 21% of the tweets. They celebrated the exclusion of trans women from female sports and were anti-hormone therapy, claiming “it is being applied too soon to minors.”
The trend of activities showed that far-right and trans-exclusionary communities were highly connected and exchanged 785 retweets from users across both communities. In addition, these accounts generated a greater proportion of tweets per user. Although they are not the largest community, they are very active and manage to make a lot of noise.
Communities in favour of LGBTI rights
Five communities favouring LGBTI+ rights were identified and analysed on the supporting side. They made up 41% of the users analysed and generated 49% of all tweets analysed.
The leading community identified in favour of LGBTI rights was the LGBTI+ communities in ES, the US, and the UK. About 17% of the users generated 23% of all the tweets analysed. This group appeared to follow the calls closely and consequently echoed them. They also spoke out against discrimination, aggression, and setbacks in Spain. They also generated positive content, for example, encouraging respect for diversity through the correct use of pronouns and support shown by allies.
The second group is the Spanish LGBTI community, which comprised 6% of users and generated 9% of the tweets. This community was notable for its reactions to the opposition accounts, mainly in response to trans-exclusionary movements and the political right in Madrid.
The LGBTQ+ activist (6% users, 7% tweets) community was observed to focus mainly on legal issues, particularly the Trans Law, which was undergoing the approval process at the National Congress and was later approved in December 2022. The conversations mainly called out conservative political positions and shared information about progress. The content from this group also featured transphobic attacks and reactions to the trans-exclusionary movement.
Fourthly, the Unidas Podemos (6% users, 5% tweets) community centred much of its conversations on calling out prejudice by conservative parties and politicians. Their reactions to the trans-exclusionary movement and the entire right-wing movement were dominant. However, they also celebrated advances in rights achieved by the government (from labour rights to sexual freedom). Prominent accounts in this community included well-known politicians from Unidas Podemos.
Similarly, the fifth community, the progressives (6% users, 5% tweets), mainly reacted to right-wing attacks on LGBT laws in Madrid and reports of transphobic attacks. It, however, also highlighted positive content that celebrated progress. This community also had prominent accounts related to parties such as PSOE and Más Madrid.
Narratives with the most impact
Specific topics dominated the conversations across the communities favoring and against LGBTI rights.
Among the anti-LGBTI camp, the trans-exclusionary community focused on several narratives, which indicates that they are highly coordinated. In contrast, the extreme right was practically monothematic. Most of its tweets concentrate on repeating the “cultural downfall” narrative in various tones, be it serious, alarming, ironic, or with false dichotomies (like opposing Trans children to children with cancer).

In contrast, the pro-trans rights communities were fragmented and lacked coordination. In addition, much of their attention was devoted to denunciations and reactions to the opposition. This predominance of reactive content implies missed opportunities to promote agendas, explicitly defend the Trans Law, and make visible positive narratives that can be useful beyond online conflict.


Going forward
Based on these findings, the campaign team concluded that:
It would be beneficial for the pro-rights communities to use the “don’t fuel them” approach in how it engages with the extreme right and the trans-exclusionary movement online. This approach urges to refrain from engaging with the opposition, and in any case, to never repeat negative frames, as they only serve to make them more salient within the public debate (and more promoted by algorithms).
Furthermore, it is also worthwhile to consider how best to move past the indignation and urgency to have more constructive conversations while reflecting on how best to respond to attacks and what forms of support would be most effective for survivors.
From the data analysed, one thing is obvious: those who focus on a single or a few narratives have more reach, despite being fewer.
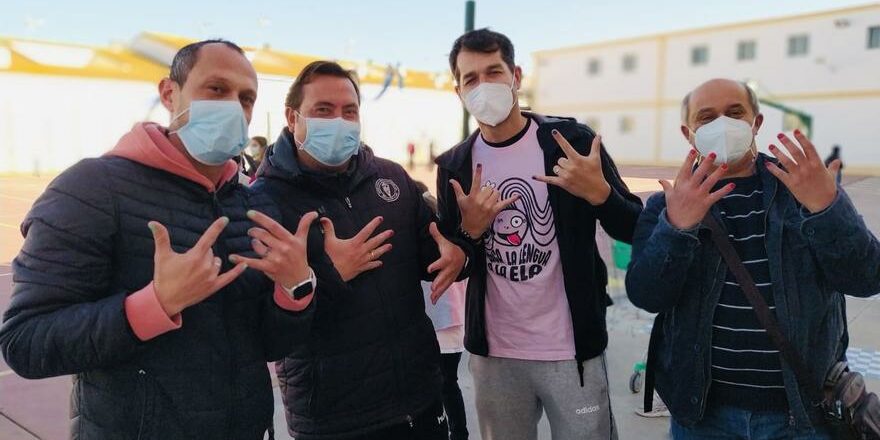
Finally, and on a more positive note, the most viral content among all pro-rights communities was a story of empathy and support for trans people. It was the story of support from a school director in Lepe, a small municipality of Andalusia, to a trans student who went to class in a skirt. Responding to transphobia, the director also wore a skirt in school, and several teachers painted their nails in support.
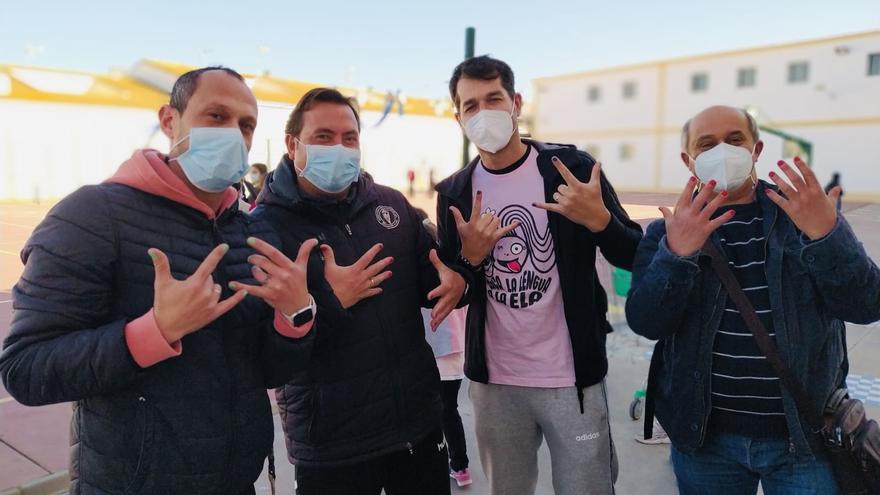

It went viral and generated international attention and support. Most importantly, it showed how an “unexpected ally” could inspire other cis people to take a more active position in defence of trans rights and how a positive perspective could reach beyond reactively mobilised communities.
Our third and last article in this series will tell you more about how the campaign was implemented.